Nyquist Sampling Theory
Introduction
Image에서의 Frequency
물리학에서 frequency는 ‘1초 동안의 주기적 변화의 횟수’ = 1/period 
그러나 image에서의 frequency는 ‘공간적으로 패턴이나 특징이 반복되는 정도’를 의미하며, pixel 간의 밝기 변화를 기반으로 계산됨.
High frequency는 밝기가 급격하게 변하는 영역(예: 선명한 가장자리)을 의미하고, low frequency는 밝기 변화가 상대적으로 완만한 영역(예: 부드러운 배경)을 의미
Sampling and Quantization
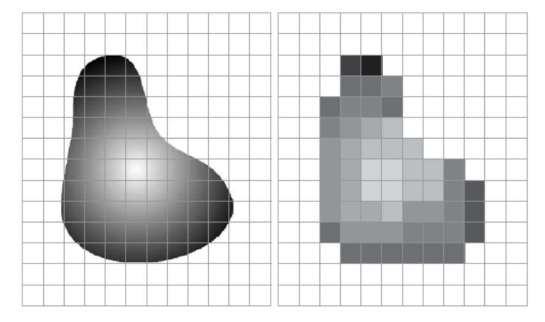
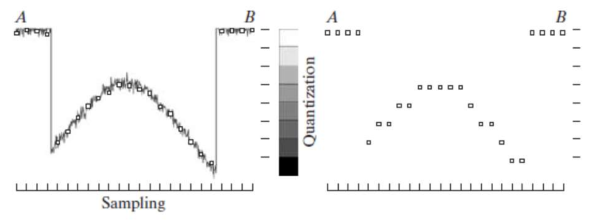
Sampling: 연속적인 이미지(아날로그 이미지)를 이산적인 픽셀 값으로 변환하는 과정
- Lower samples rate (resolution) → image가 block처럼 보임 (Blockiness)
Quantization: 샘플링된 값(픽셀의 색상값)을 특정 범위의 유한한 숫자로 제한하는 과정
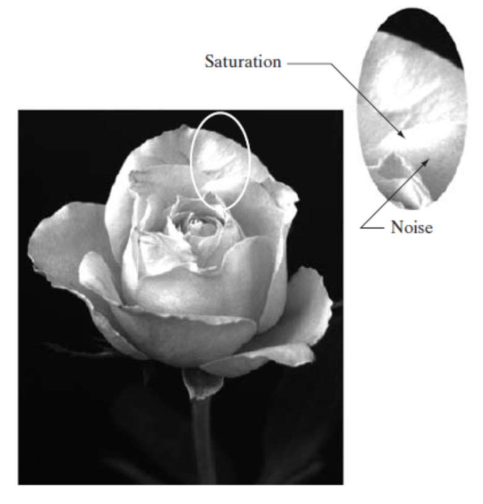
- Lower # of quantization levels → 경계와 detail이 사라지고, 특정 영역에서 색이 모두 white로 바뀌는 saturation 현상이 발생
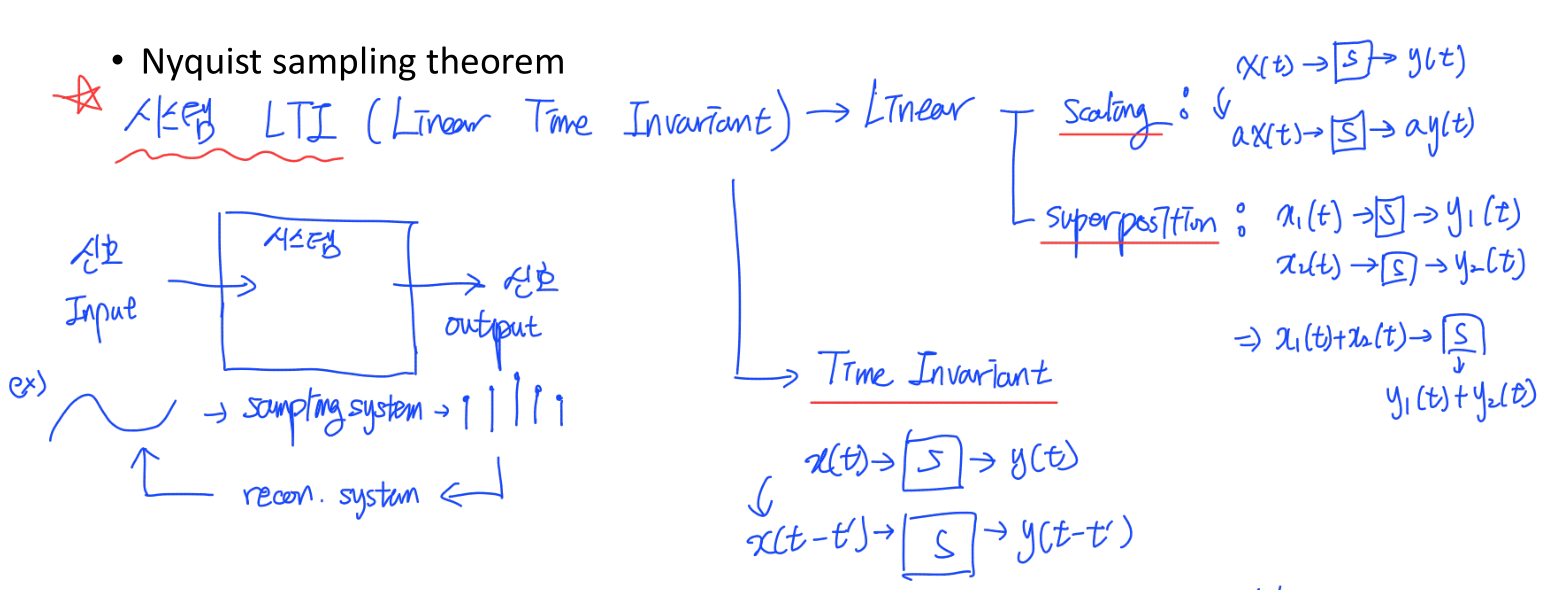
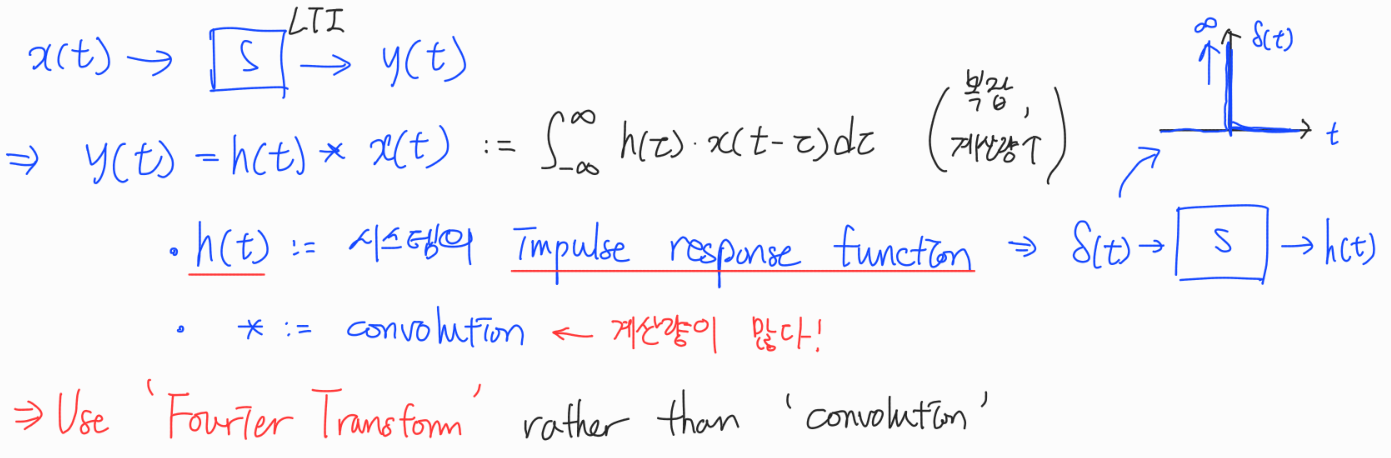
Linear Time Invariant(LTI) System
- Linear -> Scaling, Superposition
- Time Invariant
- Impulse response function
- Convolution
Fourier Transform
Fourier Transform(FT)은 주어진 신호를 다양한 frequency를 가지는 주기 함수들(sin, cos)의 합으로 나타내는 것이다. 즉, time domain을 frequency domain으로 바꿔준다.
\[X(f) = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t) e^{-j 2\pi ft} dt\]$x(t)$의 FT 변환 결과인 $X(f)$의 복소수 값의 크기는 주파수 성분의 진폭을 뜻하고, 각도는 주파수 성분의 위상을 뜻한다.
Properties of Fourier Transform
참고 공식
- $e^{jwt} = \cos wt + j \sin wt$
- $\cos wt = \frac{1}{2}(e^{jwt}+e^{-jwt})$
- $\sin wt = \frac{1}{2j}(e^{jwt}-e^{-jwt})$
$w=2\pi f$라고 하자. 그러면, $x(t)$의 FT는 다음과 같다.
\[\mathscr{F}(x(t)) = X(w) = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t) e^{-jwt} dt\]- Inverse FT는 역으로 frequency domain을 time domain으로 바꿔준다. (synthesize frequencies)
동일한 function에 대한 FT와 Inverse FT는 동일하다. (duality)
\[x(t) = \frac{1}{2\pi}\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} X(w)e^{jwt}dt\]
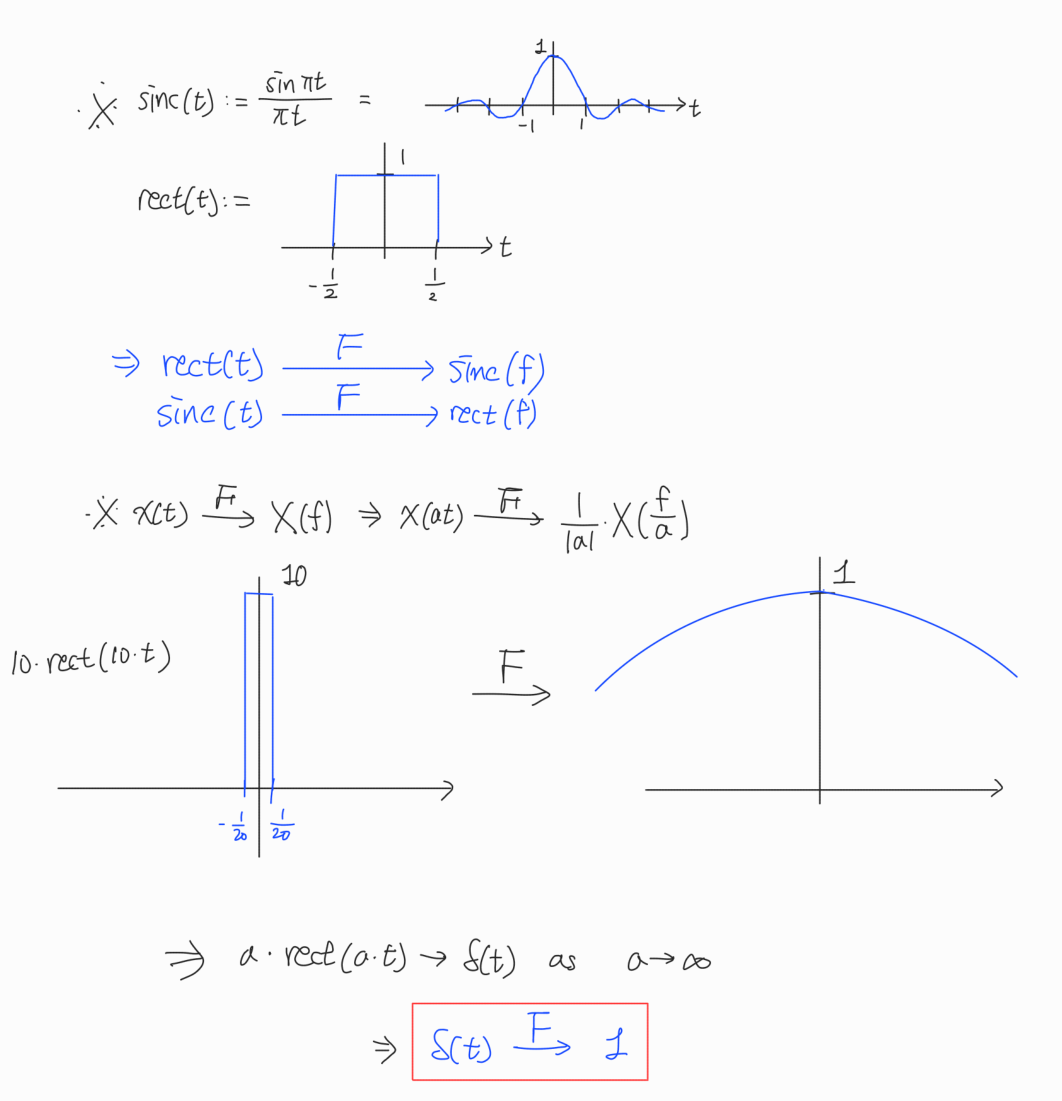
- $\delta(t)$의 Fourier transform은 1 이다.
- $\mathscr{F}(\delta(t)) = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \delta(t) e^{-jwt} dt = 1\times\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \delta(t) dt= 1$
- $x(t-t_o)$의 Fourier transform은 $X(w)e^{-jwt_0}$ 이다.
- Inverse FT 사용하면 쉽게 확인 가능
- 크기는 동일하나, $t_0$만큼 phase가 shift된다.
- Convolution 연산은 Fourier 변환 시, 곱 연산으로 바뀐다.
- $y(t)=x(t)*h(t) \rightarrow \mathscr{F}(y(t))=Y(w)=X(w)\cdot H(w)$
For a constant $a$, $\mathscr{F}(x(at))=\frac{1}{\vert a\vert}X(\frac{w}{a})$.
$\mathscr{F}(x(t)e^{jw_0t})=X(w-w_0)$.
- $\mathscr{F}(x(t))\cos w_0t=\frac{1}{2}(X(w-w_0)+X(w+w_0))$
- $\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t)\cos w_0t e^{-jwt} dt = \frac{1}{2}\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t)(e^{jw_0t}+e^{-jw_0t}) e^{-jwt} dt$
적당한 신호에 대해서는 Fourier transform을 빠르게 계산하는 법(FFT)이 개발되어 있다.
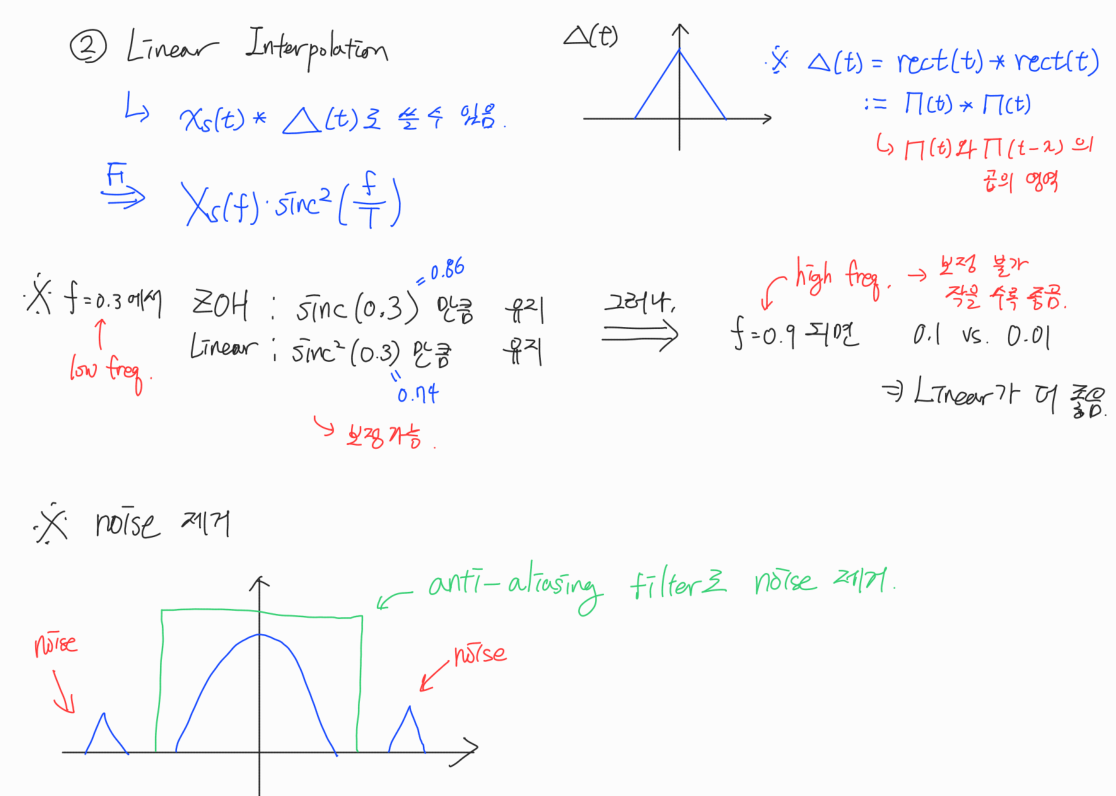
Rect and Sinc Functions
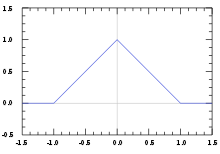
\[tri(t) = rect(t)*rect(t) \Rightarrow \mathscr{F}(tri(t)) = sinc(f)\times sinc(f) = sinc^2(f)\]역도 성립한다.
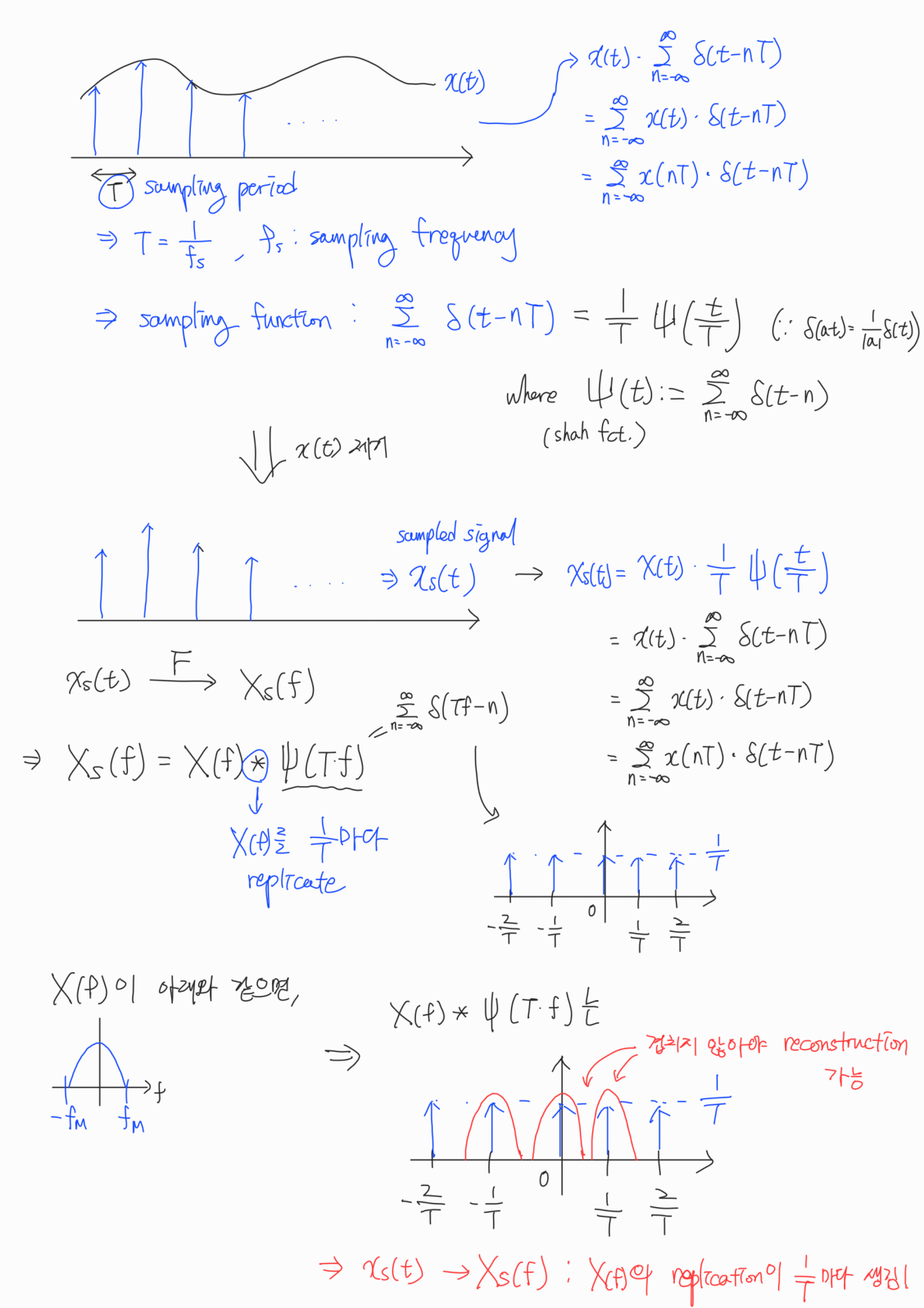
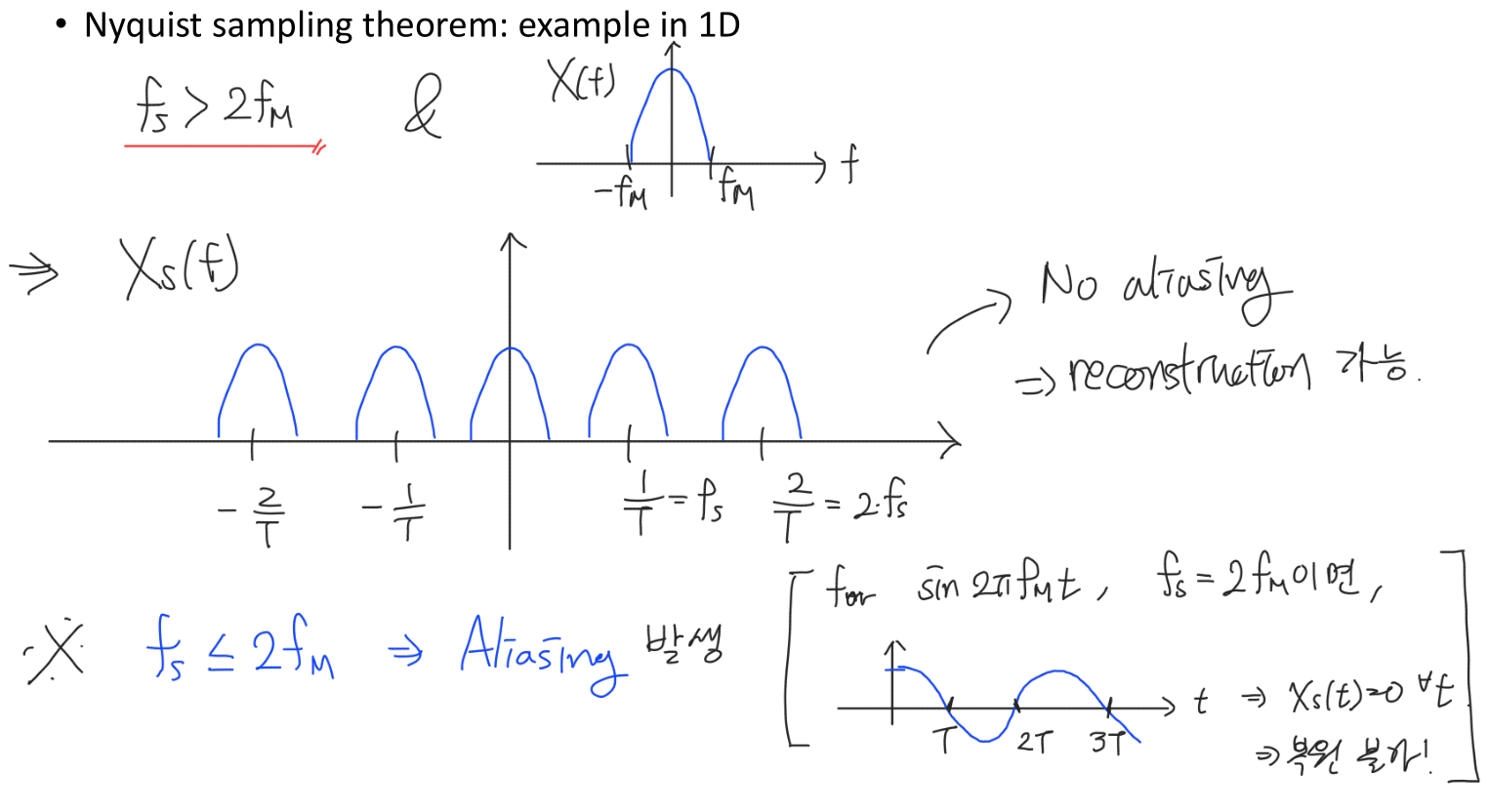
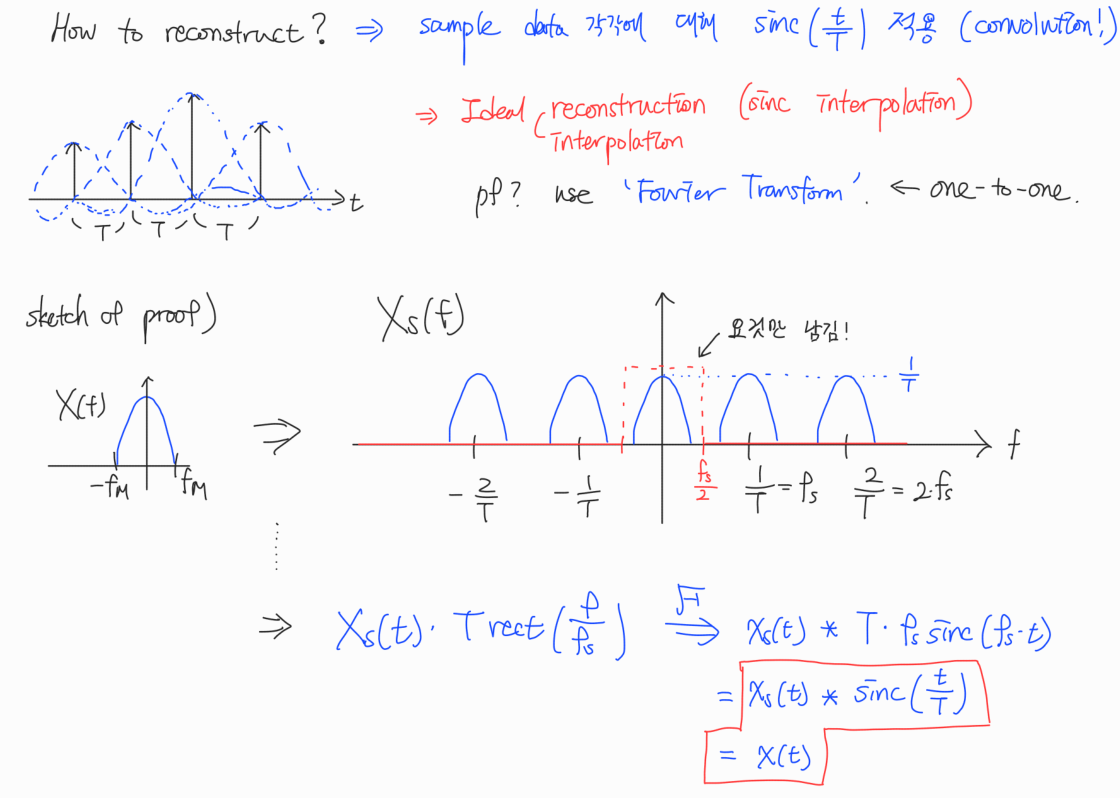
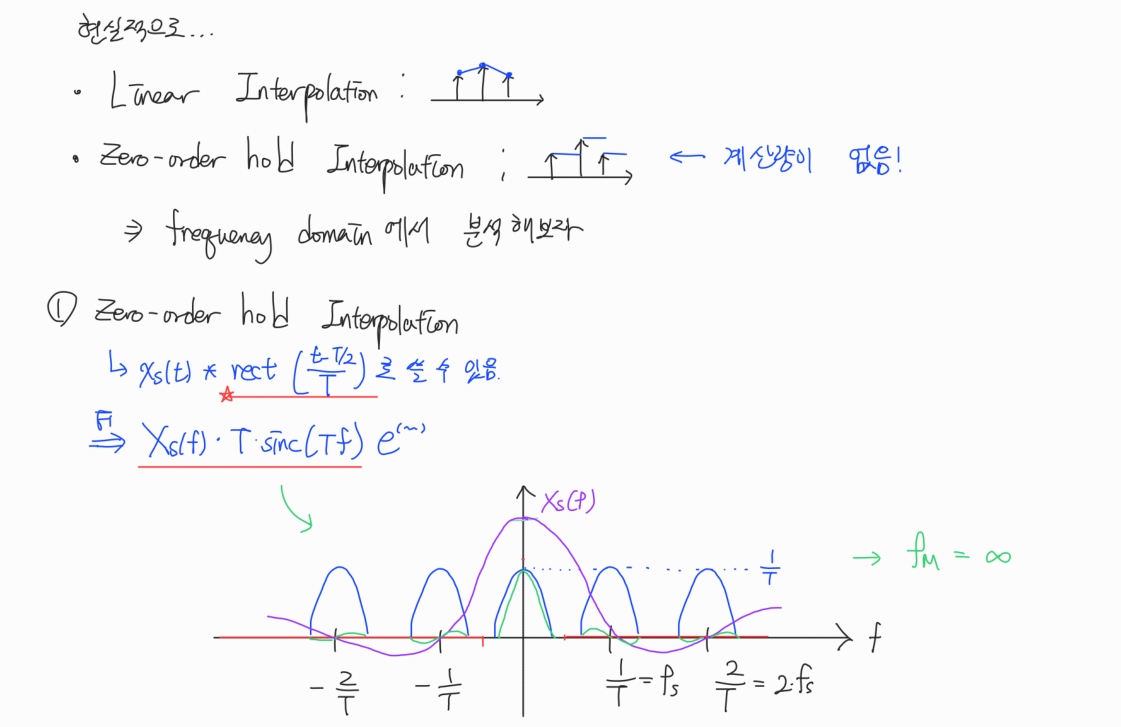
Nyquist Sampling Theory
Theorem: Nyquist Sampling
For a band-limited signal, if we sample more than twice the maximum frequency of the signal, we can perfectly reconstruct the original signal from the samples.
Nyquist Sampling Theory는 continuous signal을 completely 복원할 수 있는 sampling 방법에 대한 이론이다.