Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)
Variational autoencoder (VAE)이 sample의 분포를 미리 정해두고 이를 학습하는 explicit modeling이었다면, generative adversarial network (GAN)은 density function에 대한 가정이 필요없는 implicit modeling이다.
GAN은 다음과 같은 형태를 갖는다.
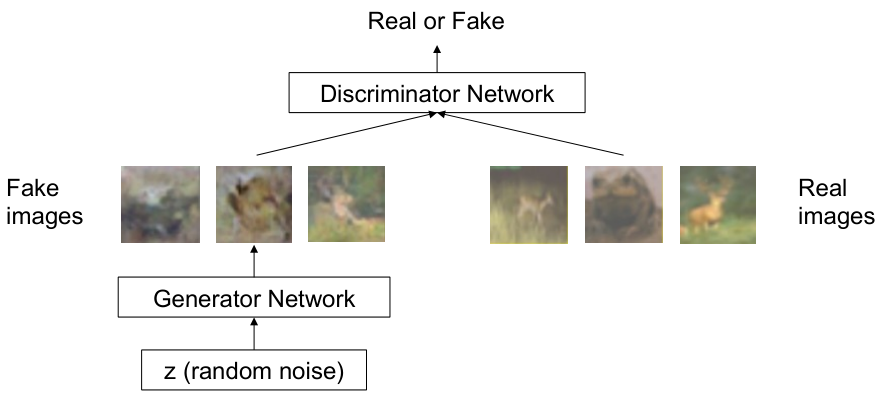
- Generator: 가짜 sample을 생성하고, discriminator를 속이는 것이 목표
- Discriminator: 진짜와 가짜 sample을 구별해내는 것이 목표
GAN은 generator와 discriminator를 동시에 학습시켜, generator가 더욱 더 정교한 sample을 생성할 수 있도록 유도한다.
Min-max Objective Function
GAN은 game-theory의 2-player game의 아이디어를 가지고 구현되어 있으며, training 역시 minmax objective function을 통해 이루어진다.
Generator $\theta_g$를 통해 생성되는 가짜 sample을 $G_{\theta_g}(z)$라고 하자. 이 때, $z$는 sampling이 쉬운 random noise로 가정한다. Discriminator $\theta_d$의 판별 결과를 $D_{\theta_d}(\cdot)$이라고 할 때, 진짜 sample로 판단하는 경우 1, 반대의 경우 0의 값을 갖는다.
이 경우, GAN의 minmax objective function은 다음과 같다.
\[\min_{\theta_g} \max_{\theta_d} \left[ \mathbb{E}_{x\sim p_{data}} \log D_{\theta_d}(x) + \mathbb{E}_{z\sim p(z)} \log (1-D_{\theta_d}(G_{\theta_g}(z))) \right]\]위 식을 살펴보면, discriminator는 $D(x)$를 1에 가깝게, $D(G(z))$를 0에 가깝게 만들려고 (즉, 가짜/진짜 여부를 잘 맞추려고) 노력할 것이고, generator는 $D(G(z))$를 1에 가깝게 만들려고 (즉, 가짜 sample을 진짜로 속이려고) 노력할 것이라는 사실을 알 수 있다.
Training GANs
GAN의 학습은 다음 두 과정을 반복적으로 수행하면서 이루어진다.
Discriminator $\theta_d$에 대해 gradient ascent 적용 ($\theta_g$ 고정)
\[\max_{\theta_d} \left[ \mathbb{E}_{x\sim p_{data}} \log D_{\theta_d}(x) + \mathbb{E}_{z\sim p(z)} \log (1-D_{\theta_d}(G_{\theta_g}(z))) \right]\]Generator $\theta_g$에 대해 gradient ascent 적용 ($\theta_d$ 고정)
\[\max_{\theta_g} \mathbb{E}_{z\sim p(z)} \log (D_{\theta_d}(G_{\theta_g}(z)))\]
Generator의 본래 loss function $\log (1-D_{\theta_d}(G_{\theta_g}(z)))$이 0 근처에서 작은 gradient 크기를 가져 학습이 잘 되지 않는 현상을 방지하기 위해, maximize 문제로 변경한다.
학습을 마친 이후에는, generator를 원하는 generative 모델로써 사용한다.
Variations of GAN
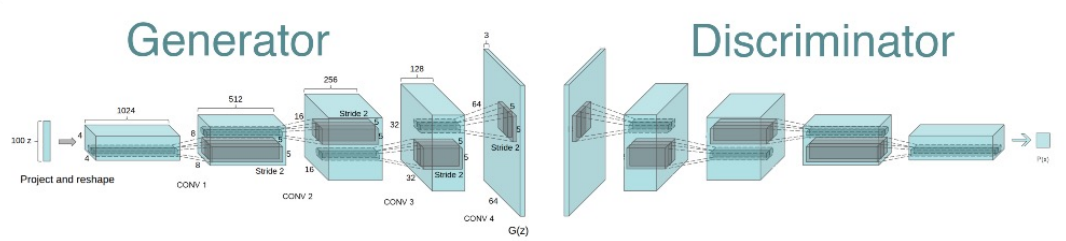
Deep Convolutional GAN
Deep convolutional GAN의 경우, generator가 deconvolutional NN, discriminator가 convolution NN으로 바뀐 것을 말한다.
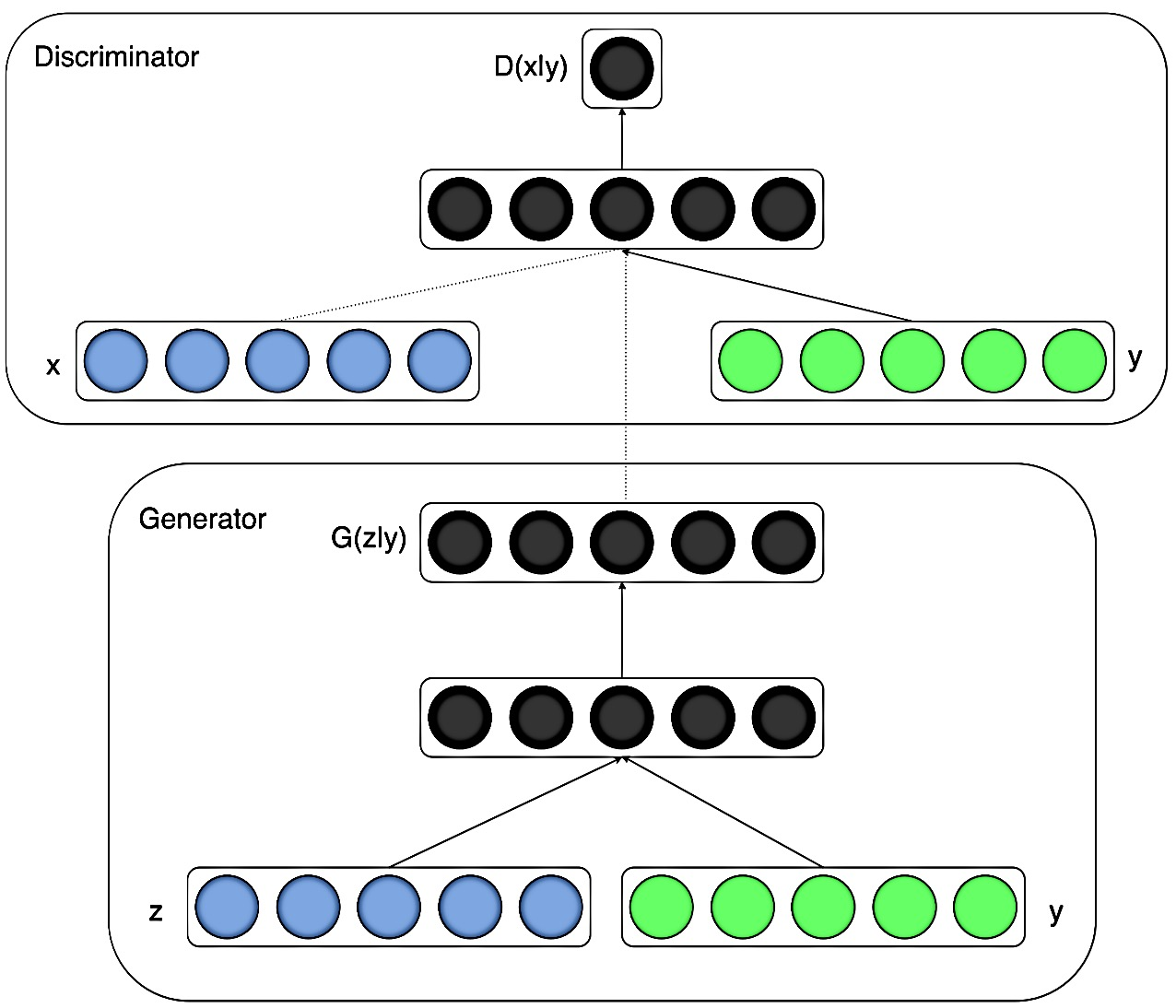
Conditional GAN
Generator와 discriminator가 extra information $y$가 주어졌을 때의 모델일 경우, 이를 conditional GAN이라고 한다.
\[\min_G \max_D \mathbb{E}_{x \sim p_{\text{data}}(x)}[\log D(x | y)] + \mathbb{E}_{z \sim p_z(z)}[\log(1 - D(G(z | y)))]\]Auxiliary Classifier GAN
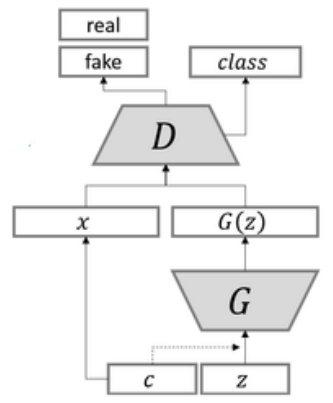
Auxiliary classifier GAN은 discriminator가 sample의 real/fake 여부를 구분하는 것과 동시에, classification을 수행한다.
$L_S$와 $L_C$를 각각 다음과 같이 정의하자.
\[L_S = \mathbb{E}[\log P(S = \text{real} \mid X_{\text{real}})] + \mathbb{E}[\log P(S = \text{fake} \mid X_{\text{fake}})]\] \[L_C = \mathbb{E}[\log P(C = c \mid X_{\text{real}})] + \mathbb{E}[\log P(C = c \mid X_{\text{fake}})]\]이 때, Auxiliary classifier GAN의 discriminator는 $L_C+L_S$를 maximize 하도록, generator는 $L_C - L_S$를 maximize하도록 학습을 진행한다.